1. BASIC
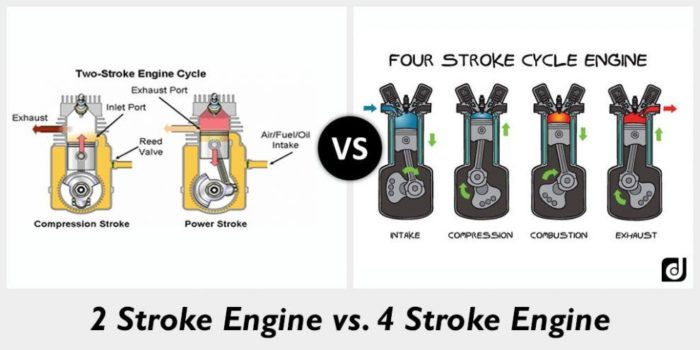
Let us differentiate between Two-stroke and four-stroke engines as per their basic function. In two-stroke engines, a cycle is completed with two strokes of the piston. While in a four-stroke engine, a single process is completed in four strokes of the piston.
The power production is done by two strokes of the piston in two strokes of the engine and by four strokes in four-stroke engines. A two-stroke lighter flywheel is used, while in a four-stroke engine heavy flywheel is required; the flywheel is used to increase the machine’s momentum.
The torque (the force that helps to rotate) in the two-stroke engine is high, and in four-stroke engines, the torque is less. The revolution of the crankshaft in a two-stroke engine is as a single revolution is made in one cycle, while in a four-stroke engine, the two crankshaft revolutions are completed in one cycle.
2. EFFICIENCY
The efficiency of the two-stroke engine is less, and the efficiency of the four-stroke engine is more; the two-stroke engine produces more smoke while the four-stroke engine produces less smoke.
In two-stroke engines, as the inlet and outlet port open simultaneously, sometimes fresh charge escapes with the exhaust gases are not always completely removed. This causes lower efficiency, and in a four-stroke engine, the fuel-air change is thoroughly utilised; thus, efficiency is higher.
The comparison of both the engines based on weight is that the two-stroke engine is lighter in weight, but the four-stroke engine is heavier.
3. WORKING
In the two-stroke engine, the charge is partially burned and mixed with burnt gases. In a four-stroke engine, the charge is entirely burned.
The engine design in the two-stroke engine is simple due to the use of ports for fuel, but in the four-stroke engine, the engine design is a bit complicated due to valves operated by chain and gear mechanism. The thermal efficiency of the two-stroke engine is less while in the four-stroke engine is greater.
4. CREATION
Lubrication is one of the important things to be done in engines, but the quantity may differ, as the two-stroke engine requires more lubrication than the four-stroke engine. The two-stroke engine makes more noise than the four-stroke engine; the reason for noise in a two-stroke engine is its construction.
The construction of a two-stroke engine is simple due to the absence of valves and valve mechanisms, but a four-stroke engine is complicated due to the presence of valves and gear.
5. COST INVOLVED
The two-stroke engine has less capital cost than the four-stroke engine, which has a high manufacturing cost. The price of vehicles also depends on this. The maintenance cost of a two-stroke engine is also less, while that of the four-stroke engine is more than two-stroke engines. The operating cost depends on this.
The starting of a two-stroke engine is easy, but starting a four-stroke engine is not that easy. The two-stroke engines are generally air-cooled, while the four-stroke engine is water-cooled.
6. PARTS OF ENGINE
The stuffing box is provided in two-stroke engines, but there is no stuffing box present in four-stroke engines. The piston rod is present in two-stroke engines, but it is not present in four-stroke engines. The four-stroke engine consists of a gudgeon pin, while it is not present in two-stroke engines.
7. STRUCTURE
The two-stroke engine has a constant pressure turbocharging system, and the four-stroke engines have a pulse turbocharging system. The two-stroke engine consists of 3 major moving parts, while the four-stroke engine consists of 9 major moving parts.
The acceleration in two-stroke engines is faster than the acceleration in four-stroke engines, which is usually slower also; the operation of the four-stroke engines is smothered, but in the two-stroke engines, it is more erratic. The crankshaft to camshaft ratio in a two-stroke engine is 1:1, and in a four-stroke engine, the balance is 1:2.
The two-stroke engines are the crosshead engines, and the four-stroke engines are trunk piston engines. In a two-stroke engine, the combustion air comes from the scavenging manifold via scavenge ports in the liner. In the four-stroke engine, the combustion air comes from the scavenging manifold via the inlet valve.
In a two-stroke engine, there is the addition of oil required and in a four-stroke engine no need of adding lubricant or oil to fuel. In a two-stroke engine, a bump or protrusion may be needed on the piston’s topside, and in a four-stroke engine, the top side of the piston is flat. The two-stroke engine is less volumetric as compared to the four-stroke engine, which is more volumetric.
8. EXAMPLES
A two-stroke engine is used where low power is required, like scooters, motorcycles, auto-rickshaw, etc., while a four-stroke engine is used where the high-power application is required like cars, trucks, etc.
Conclusion
In terms of efficiency and deciding which is better, the four-stroke engine wins anyway. It is far more efficient and also consumes less fuel. This is because the work done is equal to the four strokes of the piston while the energy is consumed just by one piston.






