
Arbitrage is a popular trading approach that involves buying and selling an asset simultaneously on one or more exchanges or brokers. The strategy can be applied across all assets, including cryptocurrencies, stocks, exchange-traded funds (ETF), bonds, and commodities. In this article, we will look at how crypto arbitrage works and highlight some popular strategies to use.
What is crypto arbitrage?
Cryptocurrencies are listed on hundreds of centralized exchanges like XBO and decentralized platforms like Uniswap and dYdX. They are also provided by peer-to-peer exchanges, where individual holders provide their preferred price.
A cryptocurrency offered by an exchange like XBO is the same as the one provided by Binance. As shown below, Binance has priced ETH/USDT at $1,313 while Coinbase has priced it at $1,309.
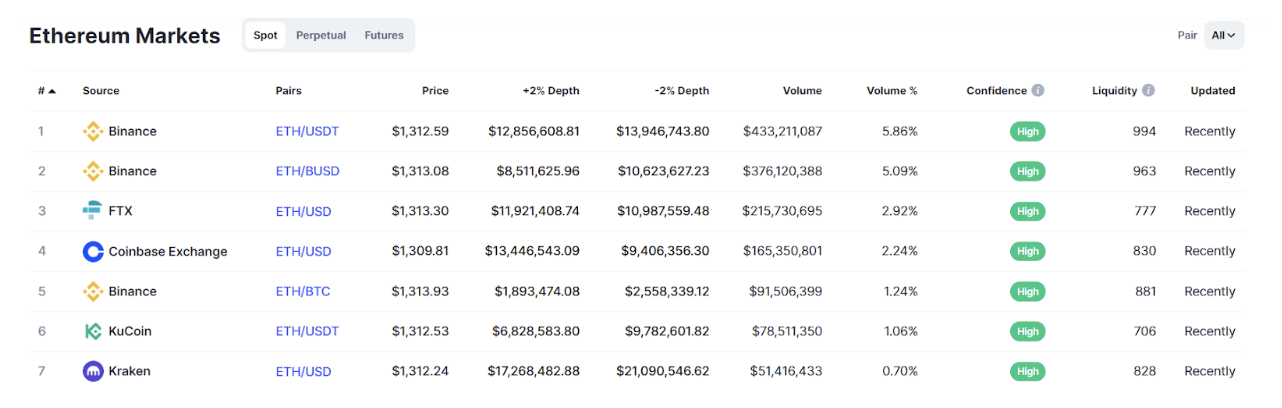
Source: CoinMarketCap
Therefore, an arbitrage trader can buy a coin at one exchange and then quickly sell it at another one at a profit. While the average profit per trade in arbitrage trading is tiny, most traders tend to execute tens of trades per day. As such, these tiny profits can add up to something bigger over time.
In the chart above, this means that a trader can buy ETH/USDT at Coinbase and then sell it at Binance for a small profit of about $3.
Spreads on centralized exchanges can be extremely tight. Therefore, most traders using the arbitrage strategy do it on peer-to-peer exchanges like Binance P2P, Local Bitcoins, and Paxful. This happens because traders on these exchanges set their own prices. As such, it is common to see extremely wide spreads on these platforms.
How crypto-arbitrage works
To understand how cryptocurrency arbitrage works, it is important to understand how these assets are determined and listed by exchanges. Like the prices of other assets such as stocks and commodities, the prices of cryptocurrencies are determined by the open interest, or demand and supply, in the market.
Ideally, higher demand versus supply will lead to a higher price, and vice versa. Therefore, the price displayed by an exchange is the one sent directly by a market participant to the order book.
Therefore, many centralized exchanges list different prices for the same asset. As such, arbitrage is a strategy where traders aim to take advantage of this pricing. For example, a trader can buy Bitcoin on one exchange and then simultaneously sell it on another exchange.
Types of crypto arbitrage trading
There are several types of arbitrage in cryptocurrency trading. The most popular ones are:
Arbitrage in P2P exchanges
A common type of arbitrage is one that happens on P2P exchanges. This strategy seeks to capitalize on the pricing disparities that exist on exchanges such as Binance P2P and Paxful.This spread is usually much wider since prices are not determined by the order book. They are instead determined by the individual seller.
As such, if the market price of Ether is at $1,300, a trader can decide to sell at $1,100 in a bid to attract a seller faster. This pricing difference happens because of the nature of competition on these P2P exchanges.
After buying the coin, the person can then list it on the same exchange at a higher price. In this case, he could price the coin at $1,200. This price is still lower than Ethereum’s market price but is also a $100 profit. A good example of this type of arbitrage is shown below.
In the first chart, the minimum buying price of ETH is $1,359,
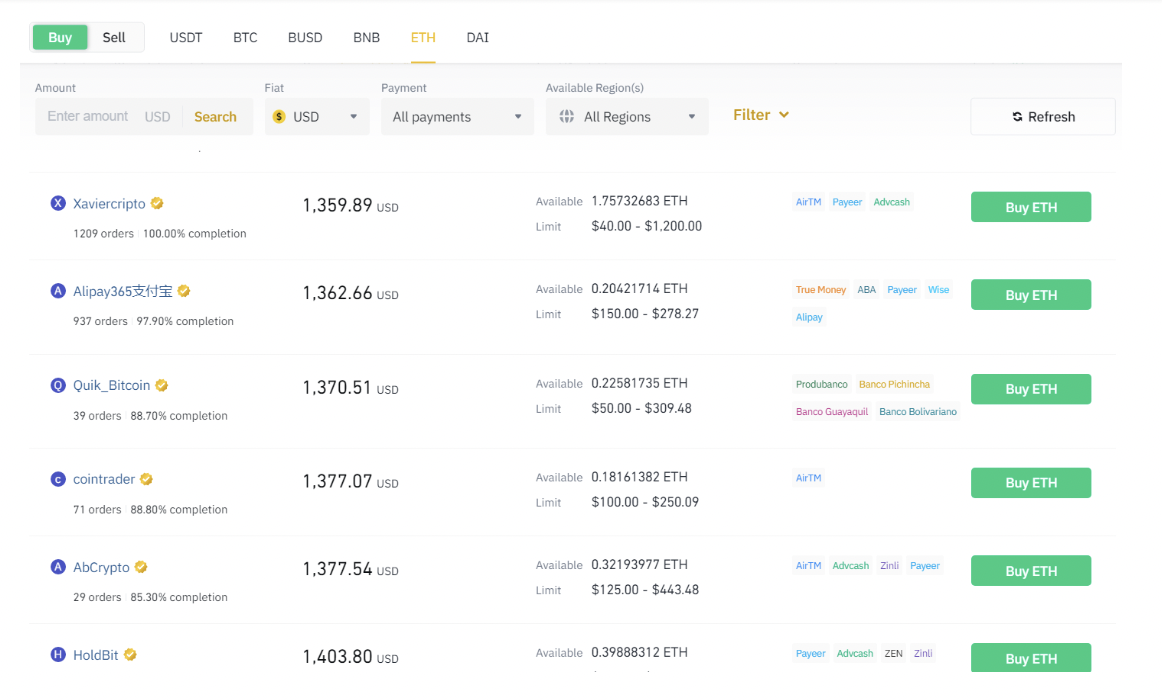
In the second chart, the maximum buying price is $1,445. Therefore, it is possible to buy ETH at $1,359 and then sell it at $1,445 and make a profit of $92.
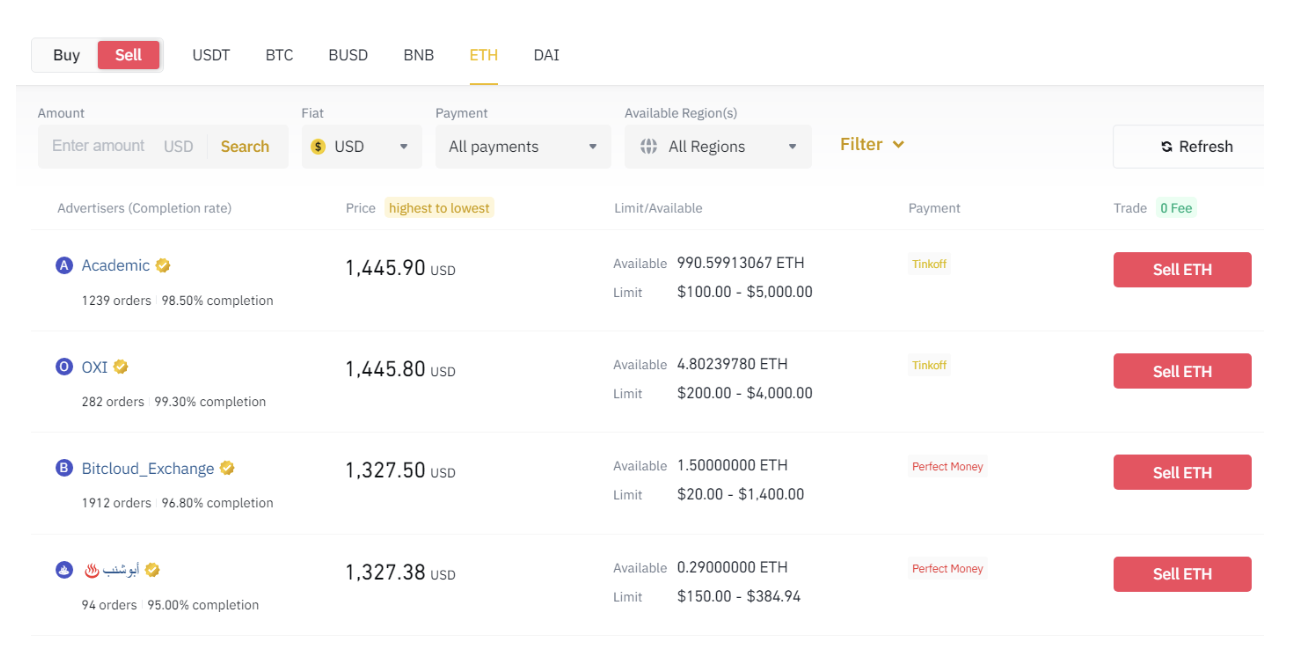
Source: https://p2p.binance.com/en/trade/sell/ETH?fiat=USD&payment=ALL
Crypto arbitrage on different exchanges
Another arbitrage strategy is one where a trader looks at the price differentials of the same asset on different exchanges. For example, assume that Bitcoin is trading at $1,312 in exchange A and $1,309 in exchange B. In this case, the trader can buy on exchange B and then sell it on the second exchange.
The main challenge of this approach is that the trader needs to have an account with both exchanges for it to work. Another main issue is that the spread is often thin and fees are substantially high in most exchanges.
A walkaround for this challenge involves holding cryptocurrencies on the two exchanges. By so doing, a trader can easily buy and sell the cryptocurrency simultaneously without suffering substantial costs. For example, assume that BTC is trading at $20,200 on a crypto exchange like XBO and $20,000 in Coinbase.
In this case, the trader can buy BTC on Coinbase and sell the Bitcoin they hold on XBO. The profit for this trade is $200.
Correlated cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrencies have a strong correlation with each other. In most periods, most digital currencies tend to follow Bitcoin’s lead. Therefore, it is possible to take advantage of this correlation by going long, or buying, one asset and shorting the other one.
For example, assume that Cardano’s ADA and Ripple’s XRP are trading at $0.45 and that the two have a correlation coefficient of near 1. After doing your analysis, you conclude that the two coins are likely to go up.
In this case, you can buy $1,000 worth of XRP and then place a short trade on ADA. If the trade works out and the correlation works out, XRP’s trade will be profitable while the latter will make a loss. In this case, the profit will be spread between the two.
DeFi arbitrage
Decentralized Finance, commonly known as DeFi, is a popular technology that makes it possible for traders to bypass centralized platforms. These companies are known for their transparency and the fact that they are non-custodial in nature.
They also provide an excellent way to use cryptocurrency arbitrage. For example, if a popular DeFi exchange like AAVE offers an APY of 5% and another one like Maker has an APY of 7%, a trader can convert their low-yielding stablecoin into a higher-yielding one. In this case, the profit will be a spread of 2%.
Crypto trading arbitrage risks
Like all other cryptocurrency trading strategies, arbitrage has its risks. For example, at times, in correlation arbitrage, there are risks that prices can end this relationship when the trade is on. This divergence is relatively common because of volatility in the cryptocurrency industry.
Another major risk in arbitrage is slippage, which is common in extremely volatile market conditions. Slippage happens when a trade is executed at a different price than the one that was placed. As such, a trader can place a buy order at $1,200, and the broker will execute it at $1,202.
Further, there is a risk that a trade will close the spread before the arbitrage is completed. For example, a trader can buy a coin at $100, hoping to sell it at $105, but the spread then narrows before it is executed.
Summary
Arbitrage is a relatively low risk trading approach in cryptocurrency trading. It involves buying and selling digital coins with the goal of benefiting from the spread. In this article, we have looked at several types of arbitrage and the risks of using this strategy in trading.






